Affect in the Wild
Emotion intelligence plays a significant role in human interactions. But when it comes to human-computer interactions, emotional intelligence still is not widely used. The rapid development of personal digital devices has opened an opportunity to integrate emotion into human-computer interactions. However, there is a gap between existing affective technologies and widespread usage of those technologies. Further, the growing concerns about user data privacy limit the adaptation of such technologies in real life.
This project focuses on bridging the gap between affective technologies and consumer devices while preserving users' data privacy. Primarily, we look into signals that can capture from consumer devices such as smart wearables to identify human affective information without sharing user-generated signals with external services while consuming a small amount of resources on user devices. In technology-wise, we explore representation learning methods and federated learning techniques to bring affect recognition to user devices.
The feature image is using graphics of people & icons form freepick.
PUBLICATIONS
Troi: Towards Understanding Users Perspectives to Mobile Automatic Emotion Recognition System in Their Natural Setting
Dissanayake V., Tang V., Elvitigala D.S., Wen E., Wu M., Nanayakkara S.C. 2022. Troi: Towards Understanding Users Perspectives to Mobile Automatic Emotion Recognition System in Their Natural Setting. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Mobile Human-Computer Interaction.
SigRep: Towards Robust Wearable Emotion Recognition with Contrastive Representation Learning.
Dissanayake, V., Seneviratne, S., Rana, R., Wen, E., Kaluarachchi, T., Nanayakkara, S.C., (2022). SigRep: Towards Robust Wearable Emotion Recognition with Contrastive Representation Learning. IEEE Access
Self-supervised Representation Fusion for Speech and Wearable Based Emotion Recognition
Dissanayake V., Seneviratne S., Suriyaarachchi H., Wen E., Nanayakkara S.C. 2022. Self-supervised Representation Fusion for Speech and Wearable Based Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of Interspeech 2022
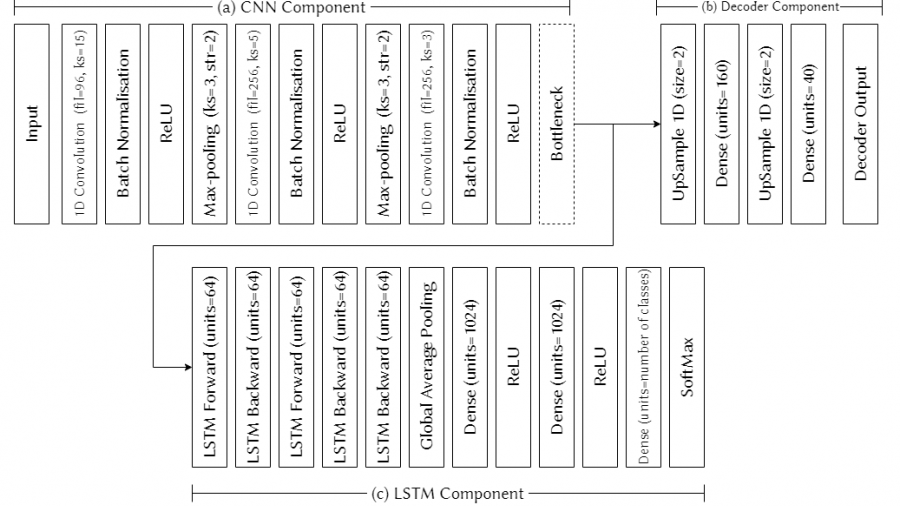
Speech Emotion Recognition ‘in the Wild’ Using an Autoencoder
Dissanayake, V., Zhang, H., Billinghurst, M. and Nanayakkara, S.C., 2020. Speech Emotion Recognition ‘in the wild' using an Autoencoder. Proc. Interspeech 2020, pp.526-530.